Npcap 是一款高性能的网络捕获和数据包分析库,作为 Nmap 项目的一部分,Npcap 可用于捕获、发送和分析网络数据包。本章将介绍如何使用 Npcap 库来实现半开放扫描功能。TCP SYN 半开放扫描是一种常见且广泛使用的端口扫描技术,用于探测目标主机端口的开放状态。由于这种方法并不完成完整的 TCP 三次握手过程,因此具有更高的隐蔽性和扫描效率。
笔者原本想为大家整理并分享如何使用Nmap工具进行端口扫描的,但觉得仅仅讲解Nmap的命令使用方法并不能让大家更好地理解其工作原理。实际上,Nmap 的底层使用的是Npcap库,因此笔者决定演示如何使用Npcap库开发一个简单的扫描功能,从而帮助大家更好地理解Nmap的原理。
首先,若使用Nmap对目标主机进行SYN扫描,只需要执行nmap -sS 39.97.203.57命令即可,等待一段时间则可获取到目标主机常规开放端口状态,若要扫描特定端口开放状态仅需要指定-p参数并携带扫描区间即可,如下命令所示;
┌──(lyshark㉿kali)-[~] └─$ sudo nmap -sS 39.97.203.57 Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-08-08 15:28 CST Nmap scan report for 39.97.203.57 Host is up (0.0038s latency). Not shown: 997 filtered tcp ports (no-response) PORT STATE SERVICE 80/tcp open http 443/tcp open https 1935/tcp open rtmp ┌──(lyshark㉿kali)-[~] └─$ sudo nmap -sS -v 39.97.203.57 -p 1-2000 Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-08-08 15:32 CST Scanning 39.97.203.57 [2000 ports] Discovered open port 80/tcp on 39.97.203.57 Discovered open port 443/tcp on 39.97.203.57 Discovered open port 1935/tcp on 39.97.203.57 Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 15:32, 7.42s elapsed (2000 total ports) Nmap scan report for 39.97.203.57 Host is up (0.0039s latency). Not shown: 1997 filtered tcp ports (no-response) PORT STATE SERVICE 80/tcp open http 443/tcp open https 1935/tcp open rtmp
Npcap库的配置非常简单,读者仅需要去到官网 下载,初次使用还需安装Npcap 1.79 installer 驱动程序,并下载Npcap SDK 1.13 对应的开发工具包,如下图所示;
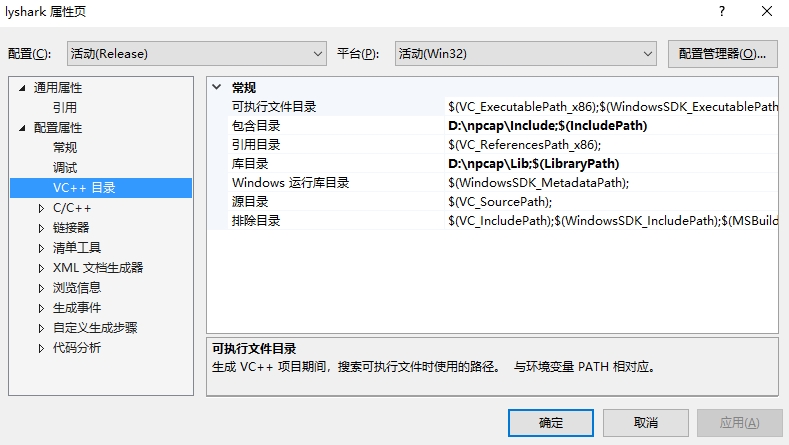
接着,读者需要自行解压SDK开发工具包,并配置VC++目录包含目录与库目录,如下图所示;
在进行开发之前,我们需要先定义三个结构体变量,首先定义eth_header数据包头,以太网包头(Ethernet Frame Header)用于传输控制信息和数据,它是数据链路层的一部分,负责在局域网中实现数据的可靠传输。
接着定义ip_header数据包头,IP头(IP Header)用于传输控制信息和数据,IP头是网络层的一部分,负责实现跨越不同网络的数据传输。
最后定义tcp_header数据包头,TCP头(TCP Header)用于传输控制信息和数据,TCP头是传输层的一部分,负责在主机之间提供可靠的、面向连接的通信。
若要发送TCP数据包,必须要构造一个完整的通信协议头,将以太网数据包头、IP数据包头、TCP数据包头封装起来即可,其定义部分如下所示,其中每一个变量均对应于协议的每一个参数。
#include <winsock2.h> #include <Windows.h> #include <pcap.h> #pragma comment(lib,"ws2_32.lib" ) #pragma comment(lib, "packet.lib" ) #pragma comment(lib, "wpcap.lib" ) struct eth_header { uint8_t dest[6 ]; uint8_t src[6 ]; uint16_t type; }; struct ip_header { uint8_t ihl : 4 , version : 4 ; uint8_t tos; uint16_t tot_len; uint16_t id; uint16_t frag_off; uint8_t ttl; uint8_t protocol; uint16_t check; uint32_t saddr; uint32_t daddr; }; struct tcp_header { uint16_t source; uint16_t dest; uint32_t seq; uint32_t ack_seq; uint16_t res1 : 4 , doff : 4 , fin : 1 , syn : 1 , rst : 1 , psh : 1 , ack : 1 , urg : 1 , res2 : 2 ; uint16_t window; uint16_t check; uint16_t urg_ptr; }; unsigned short checksum (void *b, int len) { unsigned short *buf = (unsigned short *)b; unsigned int sum = 0 ; unsigned short result; for (sum = 0 ; len > 1 ; len -= 2 ) sum += *buf++; if (len == 1 ) sum += *(unsigned char *)buf; sum = (sum >> 16 ) + (sum & 0xFFFF ); sum += (sum >> 16 ); result = ~sum; return result; }
接着需要实现两个通用函数,其中EnumAdapters用于枚举当前系统中所有的网卡信息,并输出其下标号与网卡描述信息,BindAdapters函数则用于根据用户传入的下标号对网卡进行动态绑定,函数中通过循环的方式查找网卡下标若匹配则将下标所对应的句柄存储到temp_adapter变量内,最后通过pcap_open_live实现对网卡的打开。
int EnumAdapters () { pcap_if_t *allAdapters; pcap_if_t *ptr; int index = 0 ; char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; if (pcap_findalldevs_ex(PCAP_SRC_IF_STRING, NULL , &allAdapters, errbuf) != -1 ) { for (ptr = allAdapters; ptr != NULL ; ptr = ptr->next) { ++index; if (ptr->description) { printf ("[ %d ] \t [ %s ] \n" , index - 1 , ptr->description); } } } pcap_freealldevs(allAdapters); return index; } pcap_t * BindAdapters (int nChoose) { pcap_if_t *adapters, *temp_adapter; char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; pcap_t *handle = NULL ; if (pcap_findalldevs_ex(PCAP_SRC_IF_STRING, NULL , &adapters, errbuf) == -1 ) { return NULL ; } temp_adapter = adapters; for (int x = 0 ; x < nChoose - 1 && temp_adapter != NULL ; ++x) { temp_adapter = temp_adapter->next; } if (temp_adapter == NULL ) { pcap_freealldevs(adapters); return NULL ; } handle = pcap_open_live(temp_adapter->name, 65534 , PCAP_OPENFLAG_PROMISCUOUS, 1000 , errbuf); if (handle == NULL ) { pcap_freealldevs(adapters); return NULL ; } pcap_freealldevs(adapters); return handle; }
抓包回调函数packet_handler由pcap_loop调用,当启用抓包后若句柄返回数据则会通过回调函数通知用户,用户获取到数据包header后,通过逐层解析即可得到所需要的字段,若要实现SYN快速探测则需要判断tcph标志,若标志被返回则可通过RST断开会话,并以此节约扫描时间。
如下代码,定义了一个网络数据包回调函数 packet_handler,用于处理通过 pcap 库捕获的网络数据包。函数首先打印数据包的长度,然后解析以太网头部以检查其类型是否为 IP(0x0800)。如果是 IP 数据包,进一步解析 IP 头部并打印相关信息,包括 IP 版本、头长度、源 IP 地址和目标 IP 地址。随后检查 IP 数据包的协议字段是否为 TCP(6),若是,则解析 TCP 头部并打印源端口、目标端口、序列号、确认号、头部长度、标志、窗口大小、校验和及紧急指针等信息。
void packet_handler (u_char *param, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *pkt_data) { printf ("数据包长度:%d\n" , header->len); struct eth_header *eth =struct eth_header *)(pkt_data); if (ntohs(eth->type) == 0x0800 ) { struct ip_header *iph =struct ip_header *)(pkt_data + sizeof (struct eth_header)); printf ("IP 版本: %d | " , iph->version); printf ("IP 头长度: %d | " , iph->ihl * 4 ); printf ("源IP地址: %s | " , inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr *)&iph->saddr)); printf ("目标IP地址: %s\n" , inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr *)&iph->daddr)); if (iph->protocol == 6 ) { struct tcp_header *tcph =struct tcp_header *)(pkt_data + sizeof (struct eth_header) + iph->ihl * 4 ); printf ("源端口: %d | " , ntohs(tcph->source)); printf ("目标端口: %d | " , ntohs(tcph->dest)); printf ("序列号: %u | " , ntohl(tcph->seq)); printf ("确认号: %u | " , ntohl(tcph->ack_seq)); printf ("包头长度: %d | " , tcph->doff * 4 ); printf ("标志: " ); if (tcph->fin) printf ("FIN " ); if (tcph->syn) printf ("SYN " ); if (tcph->rst) printf ("RST " ); if (tcph->psh) printf ("PSH " ); if (tcph->ack) printf ("ACK " ); if (tcph->urg) printf ("URG " ); printf ("\n" ); printf ("窗体长度: %d | " , ntohs(tcph->window)); printf ("校验和: 0x%04x | " , ntohs(tcph->check)); printf ("紧急数据指针: %d\n" , ntohs(tcph->urg_ptr)); } } printf ("\n" ); }
最后来看下主函数是如何实现的,首先通过调用EnumAdapters函数获取到网卡编号,并调用BindAdapters(4)函数绑定到指定的网卡之上,套接字的创建依然采用原生API接口来实现,只不过在调用sendto发送数据包时我们需要自行构建一个符合SYN扫描条件的数据包,在构建数据包时,以太网数据包用于指定网卡MAC地址等信息,IP数据包头则用于指定IP地址等信息,TCP数据包头则用于指定端口号信息,并仅需将tcph->syn = 1;设置为1,通过checksum计算校验和,并将校验好的packet包通过sendto函数发送到对端主机,如下所示;
int main (int argc, char * argv[]) { pcap_if_t *alldevs; pcap_t *adhandle; int i = 0 ; EnumAdapters(); adhandle = BindAdapters(4 ); SOCKET sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW); if (sock == INVALID_SOCKET) { return -1 ; } int one = 1 ; if (setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, (char *)&one, sizeof (one)) == SOCKET_ERROR) { return -1 ; } char packet[4096 ]; memset (packet, 0 , 4096 ); struct eth_header *eth =struct eth_header *)packet; struct ip_header *iph =struct ip_header *)(packet + sizeof (struct eth_header)); struct tcp_header *tcph =struct tcp_header *)(packet + sizeof (struct eth_header) + sizeof (struct ip_header)); memset (eth->dest, 0xff , 6 ); memset (eth->src, 0x00 , 6 ); eth->type = htons(0x0800 ); iph->ihl = 5 ; iph->version = 4 ; iph->tos = 0 ; iph->tot_len = sizeof (struct ip_header) + sizeof (struct tcp_header); iph->id = htons(54321 ); iph->frag_off = 0 ; iph->ttl = 255 ; iph->protocol = IPPROTO_TCP; iph->check = 0 ; iph->saddr = inet_addr("192.168.1.1" ); iph->daddr = inet_addr("39.97.203.57" ); tcph->source = htons(12345 ); tcph->dest = htons(80 ); tcph->seq = 0 ; tcph->ack_seq = 0 ; tcph->doff = 5 ; tcph->fin = 0 ; tcph->syn = 1 ; tcph->rst = 0 ; tcph->psh = 0 ; tcph->ack = 0 ; tcph->urg = 0 ; tcph->window = htons(5840 ); tcph->check = 0 ; tcph->urg_ptr = 0 ; iph->check = checksum((unsigned short *)packet, iph->tot_len); struct { uint32_t src_addr; uint32_t dst_addr; uint8_t placeholder; uint8_t protocol; uint16_t tcp_length; struct tcp_header tcp ; } pseudo_header; pseudo_header.src_addr = iph->saddr; pseudo_header.dst_addr = iph->daddr; pseudo_header.placeholder = 0 ; pseudo_header.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP; pseudo_header.tcp_length = htons(sizeof (struct tcp_header)); memcpy (&pseudo_header.tcp, tcph, sizeof (struct tcp_header)); tcph->check = checksum((unsigned short *)&pseudo_header, sizeof (pseudo_header)); struct sockaddr_in dest ; dest.sin_family = AF_INET; dest.sin_addr.s_addr = iph->daddr; if (sendto(sock, packet, iph->tot_len, 0 , (struct sockaddr *)&dest, sizeof (dest)) == SOCKET_ERROR) { return -1 ; } pcap_loop(adhandle, 10 , packet_handler, NULL ); pcap_close(adhandle); closesocket(sock); pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
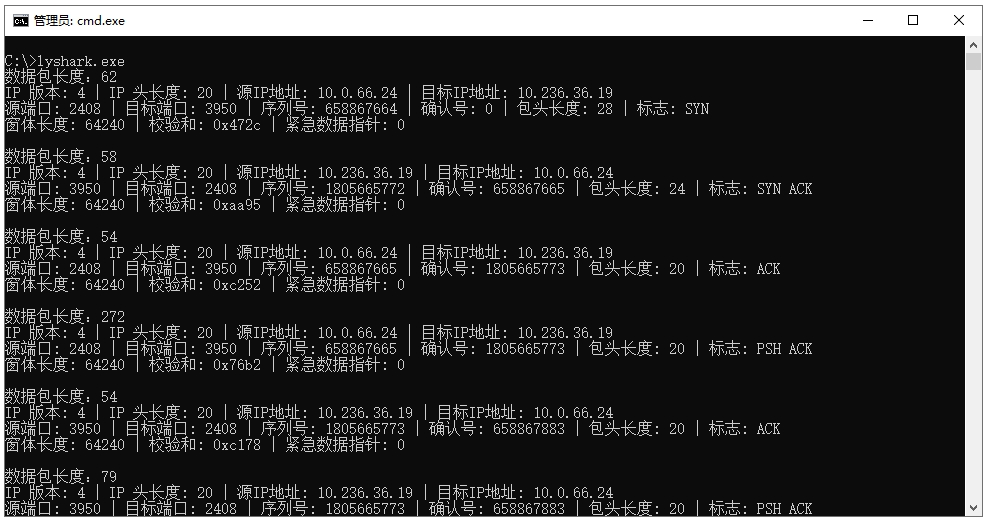
读者可自行编译并运行上述代码,当执行成功后则可看到数据包的方向及标志类型,如下图所示。