BeautifulSoup库用于从HTML或XML文件中提取数据。它可以自动将复杂的HTML文档转换为树形结构,并提供简单的方法来搜索文档中的节点,使得我们可以轻松地遍历和修改HTML文档的内容。广泛用于Web爬虫和数据抽取应用程序中。
读者如果需要使用这个库,同样需要执行pip命令用以安装:
21.8.1 属性定位链接 通过HTML属性我们可以轻松的实现对特定页面特定元素的提取,如下代码我们首先封装两个函数,其中get_page_attrs函数用于一次性解析需求,函数search_page则用于多次对页面进行解析,这两个函数如果传入attribute属性则用于提取属性内的参数,而传入text则用于提取属性自身文本。
import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupheader = {"User-Agent" :"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/71.0.3578.98" } def get_page_attrs (url,regx,attrs,timeout,type ): respon_page = [] try : respon = requests.get(url=url, headers=header, timeout=timeout) if respon.status_code == 200 : if respon != None : soup = BeautifulSoup(respon.text, "html.parser" ) ret = soup.select(regx) for item in ret: if type == "attribute" : respon_page.append( str (item.attrs[attrs] )) if type == "text" : respon_page.append(str (item.get_text())) return respon_page else : return None except Exception: return None return None def search_page (data,regx,attrs,type ): respon_page = [] if data != None : soup = BeautifulSoup(data, "html.parser" ) ret = soup.select(regx) for item in ret: if type == "attribute" : respon_page.append( str (item.attrs[attrs] )) if type == "text" : respon_page.append(str (item.get_text())) return respon_page
通过使用上述两个封装函数,读者就可以轻松的实现对特定网页页面元素的定位,首先我们通过CSS属性定位一篇文章中的图片链接,这段代码如下;
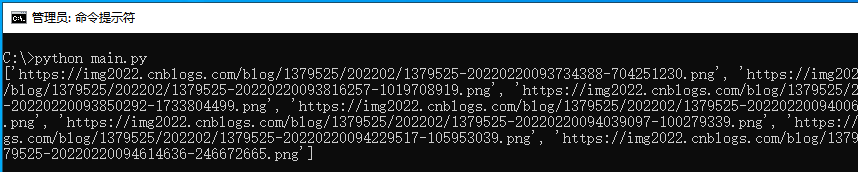
if __name__ == "__main__" : ref = get_page_attrs("https://www.cnblogs.com/LyShark/p/15914868.html" , "#cnblogs_post_body > p > img" , "src" , 5 , "attribute" ) print (ref)
当上述代码运行后,即可提取出特定网址链接内,属性#cnblogs_post_body > p > img中图片的src属性,并提取出图片属性attribute自身参数。
接着我们继续使用该函数实现定位文章列表功能,文章列表的定位同理,此处第二个参数应修改为href属性,如下代码分别使用两种方式实现对文章列表的定位功能;
if __name__ == "__main__" : ref = get_page_attrs("https://www.cnblogs.com/lyshark" , "#mainContent > div > div > div.postTitle > a" , "href" , 5 , "attribute" ) print (ref) ref = get_page_attrs("https://www.cnblogs.com/lyshark" , "div[class='day'] div[class='postCon'] div a" , "href" , 5 , "attribute" ) print (ref)
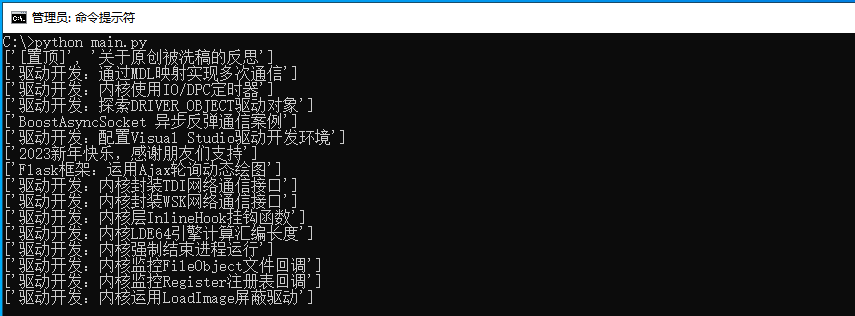
代码运行后即可输出lyshark网站中主页所有的文章地址信息,输出如下图所示;
当需要定位文章内容时,我们只需要将第二个属性更改为空格,并将第四个属性修改为text此时则代表只提取属性内的文本。
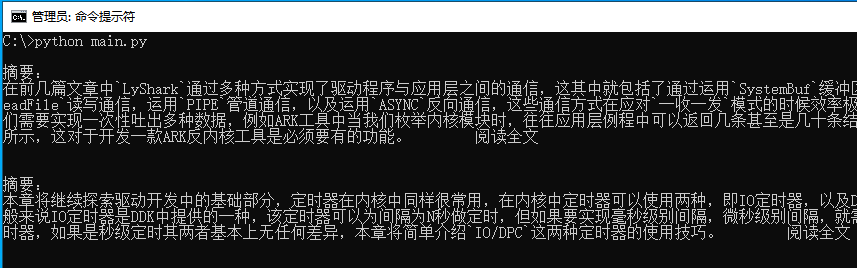
if __name__ == "__main__" : ref = get_page_attrs("https://www.cnblogs.com/lyshark" , "div[class='day'] div[class='postCon'] div[class='c_b_p_desc']" , "" , 5 , "text" ) for index in ref: print (index)
运行上述代码片段,即可提取出主页中所有的文本信息,如下图所示;
如果需要在同一个页面中多次定位那么就需要使用search_page函数了,如下代码中我们需要在一个页面内寻找两个元素,此时就需要定位两次;
if __name__ == "__main__" : respon = requests.get(url="https://yiyuan.9939.com/yyk_47122/" , headers=header, timeout=5 ) ref = search_page(respon.text, "body > div.hos_top > div > div.info > div.detail.word-break > h1 > a" , "" , "text" ) print (ref) ref = search_page(respon.text, "body > div.hos_top > div > div.info > div.detail.word-break > div.tel > span" , "" , "text" ) print (ref)
代码运行后,即可通过依次请求,分别输出该页面中的两个元素,如下图所示;
21.8.2 查询所有标签 使用find_all函数,可实现从HTML或XML文档中查找所有符合指定标签和属性的元素,返回一个列表,该函数从用于精确过滤,可同时将该页中符合条件的数据一次性全部筛选出来。
其基本语法为:
find_all(name=None , attrs={}, recursive=True , text=None , limit=None , **kwargs)
name:标签名或列表,用于查找指定标签名的元素,如果为 True 或 None,则查找所有标签元素
attrs:字典,用于指定属性名和属性值,用于查找具有指定属性名和属性值的元素
recursive:布尔值,表示是否递归查找子标签,默认为 True
text:字符串或正则表达式,用于匹配元素的文本内容
limit:整数,限制返回的匹配元素的数量
kwargs:可变参数,用于查找指定属性名和属性值的元素
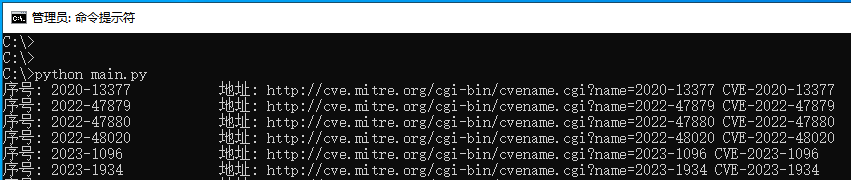
我们以输出CVE漏洞列表为例,通过使用find_all查询页面中所有的a标签,并返回一个列表,通过对列表元素的解析,依次输出该漏洞的序号,网址,以及所对应的编号信息。
import reimport requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupheader = {"User-Agent" :"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/71.0.3578.98" } if __name__ == "__main__" : url = "https://cassandra.cerias.purdue.edu/CVE_changes/today.html" new_cve = [] ret = requests.get(url=url, headers=header, timeout=5 ) soup = BeautifulSoup(ret.text, 'html.parser' ) for index in soup.find_all('a' ): href = index.get('href' ) text = index.get_text() cve_number = re.findall("[0-9]{1,}-.*" ,index.get_text()) print ("序号: {:20} 地址: {} CVE-{}" .format (text,href,cve_number[0 ]))
读者可自行运行上述代码,即可匹配出当前页面中所有的CVE漏洞编号等,如下图所示;
21.8.3 取字串返回列表 在BeautifulSoup4中,stripped_strings是一个生成器对象,用于获取HTML标签内所有文本内容的迭代器。它会自动去除每个文本的前后空格和换行符,只返回纯文本字符串。stripped_strings可以用于处理HTML文档中的多行文本、空格等特殊符号,也可用于将元素下面的所有字符串以列表的形式返回。
import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupheader = {"User-Agent" :"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/71.0.3578.98" } if __name__ == "__main__" : ret = requests.get(url="https://www.cnblogs.com/lyshark" , headers=header, timeout=3 ) text = str (ret.content.decode('utf-8' )) bs = BeautifulSoup(text, "html.parser" ) ret = bs.select('#mainContent > div > div > div.postTitle > a > span' ) for i in ret: string_ = list (i.stripped_strings) print (string_)
运行后即可获取选中元素的字符串内容,并通过list将其转换为列表格式,如下图所示;
通过find_all以及stripped_strings属性我们实现一个简单的抓取天气的代码,以让读者可以更好的理解该属性是如何被使用的,如下代码所示;
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupimport requestshead = {'user-agent' : 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/71.0.3578.98 Safari/537.36' } ret = requests.get(url="http://www.weather.com.cn/textFC/beijing.shtml" , headers=head, timeout=3 ) text = str (ret.content.decode('utf-8' )) bs = BeautifulSoup(text,"html.parser" ) bs.find_all('div' ,class_='conMidtab' )[1 ] tr = bs.find_all('tr' )[2 :] for i in tr: td = i.find_all('td' ) city_td = td[0 ] city = list (city_td.stripped_strings)[0 ] temp = td[-5 ] temperature = list (temp.stripped_strings)[0 ] print ('城市:{} 温度:{}' .format (city,temperature))
我们以提取北京天气为案例,当运行代码后即可取出北京市所有地区的气温数据,如下图所示;